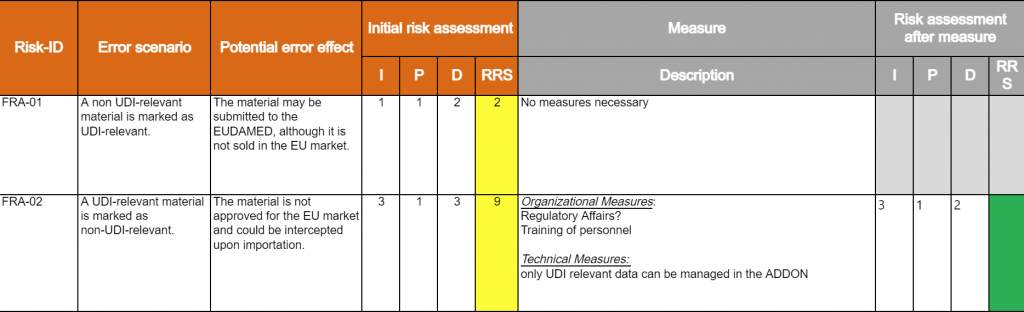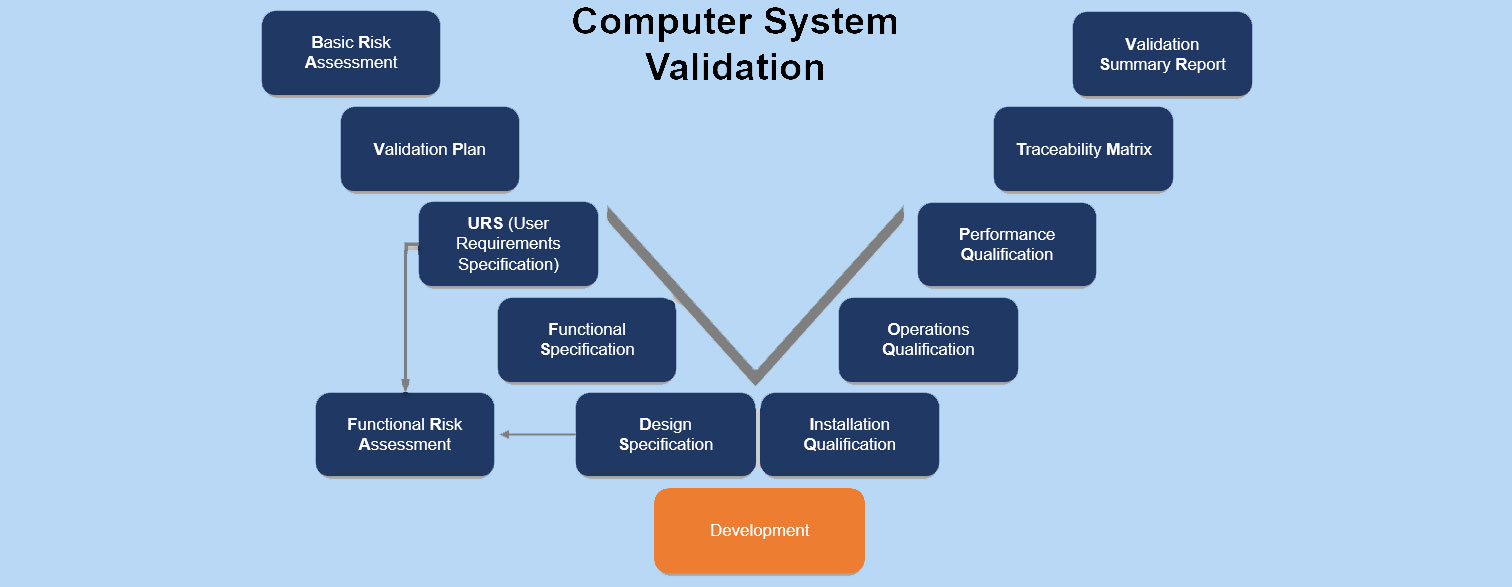
Computer System Validation – CSV
Computer System Validation refers to a documented process that ensures a computerized system does exactly what it was designed to do, in a consistent and reproducible manner.
The validation process provides documented evidence that the system consistently meets its predefined requirements and is suitable for its intended use. Validations can be used in various types of GxP-regulated environments:
- Sterility
- Cleaning
- Method
- Process validation
Why is Computer System Validation important?
Particularly for pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers, Computer System Validation is relevant as it assesses the transparency, quality, and patient safety of the system. It always applies:
- Avoiding dangers and risks to human health and life
- Avoiding product defects and their impact on human health and life
- Ensuring high-quality products through extensive testing and a controlled IT operation
- Minimizing the risk of malfunctions and failures through controlled IT operations and transparent IT processes
By implementing Computer System Validation, you also ensure compliance with national and international regulations and can cover the following critical guidelines:
- ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR 820, FDA 21 CFR Part 11, SFDA, etc.
- Reliable and safe (manufacturing) processes
- Proof of activities to comply with GxP-critical processes
In the long term, Computer System Validation also helps reduce costs:
- Low maintenance effort through the use of quality and project management standards
- Low maintenance effort and costs in change management through transparency and reliable system documentation
- Low costs in the development and manufacturing of products through the use of reliable software and processes
IQ, OQ, and PQ in the context of Computer System Validation
The acronyms stand for:
- IQ: Installation Qualification
- OQ: Operational Qualification
- PQ: Performance Qualification.
These qualifications encompass aspects of software validation and qualification
-
IQ:
- Hardware Installation Qualification: The documented evidence that
- the system is designed and built according to its specifications,
- the system is properly installed,
- the system fulfills its defined purpose,
- the installation is transparent,
- the installation is repeatable/reproducible
- Software Installation Qualification:
- is the installation guideline for the computer system with company-specific settings
and parameters - is used as a checklist and documentation for correct installation,
- should be reused for each installation of the computer system (clients, etc.),
- provides standardization of the CS and is suitable for repeated use of validation documentation in multiple systems,
- each installation of the CS is identical, transparent, and repeatable/reproducible.
- is the installation guideline for the computer system with company-specific settings
- Hardware Installation Qualification: The documented evidence that
-
OQ:
- Operational Qualification (OQ) is conducted after each IQ protocol is completed. The purpose of the OQ is to verify that the equipment’s performance meets the user requirements specification within the operating ranges specified by the manufacturer. In practice, this means identifying and testing equipment features that can affect the quality of the final product.
- During the OQ, all elements of the test plan are tested and their performance is thoroughly documented. As this is a prerequisite for equipment and system acceptance, it can only be performed after the IQ has been completed.
- In general, the OQ serves as a detailed review of hardware or software commissioning, operation, maintenance, cleaning, and safety procedures (if and where applicable). Each unit of hardware and software must be demonstrated to operate within specified limits.
-
PQ:
- The final step in equipment qualification is PQ. In this phase, the qualification and validation team verifies and documents that the equipment operates with reproducible results within a specified working range under simulated real-world conditions. Instead of testing components and equipment individually, they are tested in the PQ as part ofa whole process.
- However, before the qualification begins, the team must create a detailed test plan based on the process description. It is important to know that the quality of the qualification largely depends on the quality of the test plan. This is an area where an external specialist can (and often should) be brought in to ensure thoroughness and accuracy.
- The Process Performance Qualification (PPQ) protocol is a fundamental part of process validation and qualification. The purpose is to ensure continuous product quality by documenting performance over a specified period for certain processes.
Our Service Portfolio
- Risk-based validation
- Validation of SAP software components and self-developed SAP applications
- Validation according to ISO 13485
- Risk assessment
- Test script creation, test execution
- Execution of validation
- IQ/OQ/PQ